Difference between revisions of "Troubleshoot FTP"
m (→Credentials / Passwords) |
(→Ubuntu) |
||
| Line 168: | Line 168: | ||
*Restart FTP service. | *Restart FTP service. | ||
| − | <pre> | + | <pre>service vsftpd restart</pre> |
*Enable and disable are not available due to this service being in the Upstart scripts. | *Enable and disable are not available due to this service being in the Upstart scripts. | ||
Revision as of 19:08, 1 April 2016
Note: It seems that greater than 90% of FOG FTP problems are caused by bad/mismatched credentials. Because of this, we recommend skipping straight to the Credentials / Passwords section first.
Contents
- 1 FTP's roles in FOG
- 2 Testing FTP
- 3 FTP Service
- 4 FTP Settings File
- 5 Disable & Verify Firewall
- 6 Credentials / Passwords
- 7 Interface
- 8 FTP Path
- 9 Permissions
- 10 Common problems and fixes
- 10.1 My problem isn't in the WiKi!
- 10.2 Image Size on server: 0
- 10.3 You must first upload an image to create a download task
- 10.4 Images stuck in /images/dev
- 10.5 Updating Database...Failed
- 10.6 Large Image - Connection time out during Delete, Upload, and Replication
- 10.7 Images won't finish uploading, won't go past "Clearing ntfs flag"
FTP's roles in FOG
The primary purpose is moving & renaming image files in the /images/dev folder to the /images folder at the end of an image capture. FTP is not used for image upload or download because NFS is faster. FTP is also used to download kernels and delete images. FTP is also used to report "Image Size: ON SERVER". FTP is also used to ensure the image you wish to deploy exists before starting an image deployment.
FTP should be able to read, write, and delete in /images/dev and /images.
Testing FTP
Try to get a file with Linux:
These commands are NOT done on your FOG server, they are done on another Linux machine (this example uses Fedora).
To explain what's happening below in the code box,
- Create a test file with some data in it to send later.
- Start ftp (may need installed first).
- Open connection to FOG server.
- Provide username.
- Provide password.
- Change to /images directory.
- List directory contents.
- Upload file.
- List directory contents to verify.
- Download the file.
- Delete the file.
- Exit ftp.
[administrator@D620 ~]$ echo 'some text here to send later' > test.txt [administrator@D620 ~]$ ftp ftp> open 10.0.0.3 Connected to 10.0.0.3 (10.0.0.3). 220 (vsFTPd 3.0.2) Name (10.0.0.3:administrator): fog 331 Please specify the password. Password: 230 Login successful. Remote system type is UNIX. Using binary mode to transfer files. ftp> cd /images 250 Directory successfully changed. ftp> ls 227 Entering Passive Mode (10,0,0,3,204,176). 150 Here comes the directory listing. drwxrwxrwx 2 0 0 4096 Apr 10 03:38 Optiplex745WinXPconfiguredApril2015 drwxrwxrwx 2 0 0 4096 Apr 10 03:39 dev drwxrwxrwx 2 0 0 16384 Apr 07 01:58 lost+found drwxrwxrwx 2 0 0 4096 Apr 08 00:59 postdownloadscripts 226 Directory send OK. ftp> put test.txt local: test.txt remote: test.txt 227 Entering Passive Mode (10,0,0,3,132,59). 150 Ok to send data. 226 Transfer complete. 29 bytes sent in 0.000114 secs (254.39 Kbytes/sec) ftp> ls 227 Entering Passive Mode (10,0,0,3,118,48). 150 Here comes the directory listing. drwxrwxrwx 2 0 0 4096 Apr 10 03:38 Optiplex745WinXPconfiguredApril2015 drwxrwxrwx 2 0 0 4096 Apr 10 03:39 dev drwxrwxrwx 2 0 0 16384 Apr 07 01:58 lost+found drwxrwxrwx 2 0 0 4096 Apr 08 00:59 postdownloadscripts -rw-r--r-- 1 1000 1000 29 Apr 30 00:29 test.txt 226 Directory send OK. ftp> get test.txt local: test.txt remote: test.txt 227 Entering Passive Mode (10,0,0,3,190,81). 150 Opening BINARY mode data connection for test.txt (29 bytes). 226 Transfer complete. 29 bytes received in 0.000529 secs (54.82 Kbytes/sec) ftp> delete test.txt 250 Delete operation successful. ftp> exit 421 Timeout. [administrator@D620 ~]$
Try to get a file with Windows:
Explanation of the code below:
- Create a file with some data
- Start FTP
- Open connection to FOG server
- Enter username
- Enter password
- Upload file
- List directory to verify
- Download file
- Close connection
- Close FTP.
c:\SomeFolder>echo This is a bit of text to throw into a file > text.txt c:\SomeFolder>ftp ftp> open 10.0.0.3 Connected to 10.0.0.3. 220 (vsFTPd 3.0.2) User (10.0.0.3:(none)): fog 331 Please specify the password. Password: 230 Login successful. ftp> put text.txt 200 PORT command successful. Consider using PASV. 150 Ok to send data. 226 Transfer complete. ftp: 45 bytes sent in 0.00Seconds 22.50Kbytes/sec. ftp> ls 200 PORT command successful. Consider using PASV. 150 Here comes the directory listing. text.txt 226 Directory send OK. ftp: 10 bytes received in 0.00Seconds 10.00Kbytes/sec. ftp> get text.txt 200 PORT command successful. Consider using PASV. 150 Opening BINARY mode data connection for text.txt (45 bytes). 226 Transfer complete. ftp: 45 bytes received in 0.00Seconds 45000.00Kbytes/sec. ftp> close 221 Goodbye. ftp> quit c:\SomeFolder>
FTP Service
Fedora 20/21
- Check the status of FTP with
systemctl status vsftpd.service(should be on and green, no errors, and enabled)
- stop, start, disable and enable FTP service.
systemctl stop vsftpd.service systemctl start vsftpd.service systemctl disable vsftpd.service systemctl enable vsftpd.service
- Test that it’s functioning by using the testing instructions at the top of this article additionally, if you open a web browser and go to
ftp://x.x.x.x
- Use fog / your-fog-account-Password for the credentials
- You should see “Index of /”
Ubuntu
- Restart FTP service.
service vsftpd restart
- Enable and disable are not available due to this service being in the Upstart scripts.
- Test that it’s functioning by using the testing instructions at the top of this article additionally, if you open a web browser and go to
ftp://x.x.x.x
- Use fog / your-fog-account-Password for the credentials
- You should see “Index of /”
FTP Settings File
Fedora 20/21:
Location:
/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
To display file:
cat /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
It should look a lot like this:
anonymous_enable=NO local_enable=YES write_enable=YES local_umask=022 dirmessage_enable=YES xferlog_enable=YES connect_from_port_20=YES xferlog_std_format=YES listen=YES pam_service_name=vsftpd userlist_enable=NO tcp_wrappers=YES seccomp_sandbox=NO
To edit:
vi /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
Explanation of settings:
man vsftpd.conf
Ubuntu
Location:
/etc/vsftpd.conf
To display file:
cat /etc/vsftpd.conf
It should look a lot like this:
anonymous_enable=NO local_enable=YES write_enable=YES local_umask=022 dirmessage_enable=YES xferlog_enable=YES connect_from_port_20=YES xferlog_std_format=YES listen=YES pam_service_name=vsftpd userlist_enable=NO tcp_wrappers=YES seccomp_sandbox=NO
To edit:
vi /etc/vsftpd.conf
Explanation of settings:
man vsftpd
Instructions on using Vi: Vi
Disable & Verify Firewall
Fedora 20/21/22/23
Disable/stop Firewall
systemctl disable firewalld.service
systemctl stop firewalld.service
Can be undone with "start" and "enable".
Check Firewall in Fedora 20/21/22/23
systemctl status firewalld.service
Fedora 16
Add /bin/bash to /etc/shells as the vsftpd yum install does not do it correctly causing tftp timeout message
Debian/Ubuntu
sudo iptables -L
If disabled, the output should look like this:
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
Disable Ubuntu Firewall
sudo ufw disable
Disable Debian Firewall
iptables -F iptables -X iptables -t nat -F iptables -t nat -X iptables -t mangle -F iptables -t mangle -X iptables -P INPUT ACCEPT iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT iptables -P FORWARD ACCEPT
Other debian settings:
/etc/hosts.deny
This setting in the above file will deny traffic from any source except locally:
ALL:ALL EXCEPT 127.0.0.1:DENY
Comment out this line like so:
#ALL:ALL EXCEPT 127.0.0.1:DENY
Windows 7
Start -> Control Panel -> View by "Small icons" -> Windows Firewall -> Turn Windows Firewall On or Off -> Turn off all three.
Configuring firewall on Linux
To set the firewall for Linux to only allow what is necessary, please see the FOG security article.
Credentials / Passwords
There are a few places where all the credentials (on a standard install) should match exactly.
- Web Interface -> Storage Management -> [Your storage node] -> Management Username & Management Password
- Web Interface -> FOG Configuration -> FOG Settings -> TFTP Server -> FOG_TFTP_FTP_USERNAME & FOG_TFTP_FTP_PASSWORD
- The local 'fog' user's password on the Linux FOG server
- /opt/fog/.fogsettings -> password (For recent FOG Trunk versions only. 1.2.0 does not have this setting. 1.3.0 will though.)
All four of those should match (again, on a standard installation).
To change the password of the local fog user:
sudo passwd fog
To edit /opt/fog/.fogsettings:
vi /opt/fog/.fogsettings
Instructions on using Vi: Vi
Note: For FOG Trunk/FOG 1.3.0 users, if the password field inside of the /opt/fog/.fogsettings file is set incorrectly, every time you re-run the FOG installer, it will set the local fog user's password to this incorrect password. It's important to set the password correctly in all of the above listed areas.
Interface
The interface defined within storage management for the storage node you are using must be correct for image moving at the end of an upload (from dev to images).
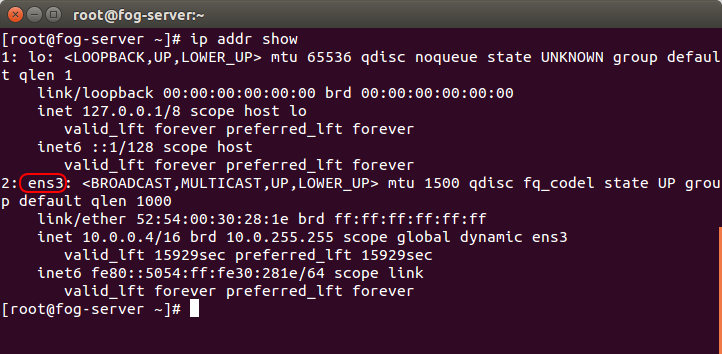
At CLI, you can find the correct interface name by typing ip addr show In the output will be the correct interface name. This is pictured below. In a multi-interface system, there will be multiple interfaces listed. You'll just need to pick the right one. Looking at the IP address assigned to the interface is the first way to determine the correct interface.
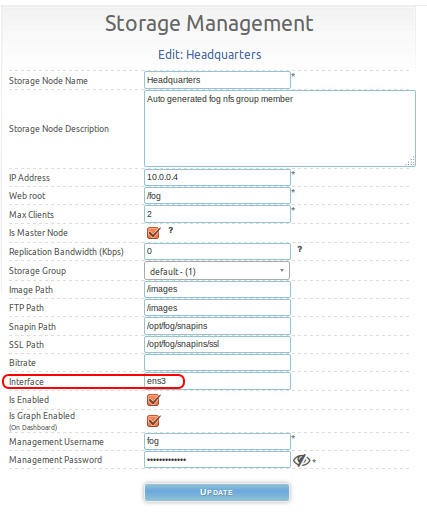
You must set this interface name inside storage management if it's not already set correctly. This problem is probably specific to FOG 1.2.0 and older because the default storage node used the default value of eth0. This is fixed in 1.3.0. Setting the proper interface name in storage management is pictured below.
FTP Path
The FTP Path is the exact path used to interact with the image files via FTP. This must be set correctly. You can find the the settings here:
- Web Interface -> Storage Management -> [Your storage node] -> FTP Path
Most of the time, the FTP Path will be the same as the Image Path. Synology NAS devices will have a different FTP Path than the Image path, typically the root directory in the Image Path is excluded from the FTP Path on Synology NAS devices.
Permissions
The credentials used for this:
Storage Management -> Storage Node -> Management Username / Management Password
Should exactly match the ownership of the /images directory and all of it's contents. The path should also match the actual path to your images directory.
You can check the permissions on all your image files with this:
ls -laR /images
You can enable all permissions (just for troubleshooting) on the /images directory recursively like this:
sudo chmod -R 777 /images
Normally, /images and all of it's contents should be owned by the local fog user. Whoever the owner is, that's the credentials you should use in you're storage node username / password fields.
You can set ownership like this:
sudo chown -R fog:root /images
Common problems and fixes
My problem isn't in the WiKi!
If you have a problem with FOG, or have a solution to a problem with FOG, please visit the forums for help or to report your solution. We try to keep the WiKi updated with things found in the forum. You can visit the forum here: FOG Forums
Image Size on server: 0
This is a common problem, and is almost always due to FTP credentials being incorrect. Please see the "Credentials" section above.
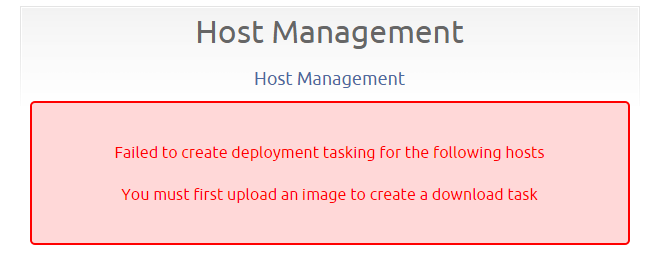
You must first upload an image to create a download task
You may get this message when you try to deploy an image to computers.
FTP is used to validate that an image exists before creating an image task. When an image does exist, but can't be verified as existing, you will receive the above error. This can be caused by incorrect credentials, permissions, or when the storage node's FTP Path field is blank or incorrect. It's possible that Firewall could be blocking FTP as well.
From what the FOG Community has seen in the forums, most people who receive this error have mismatched credentials.
Please see these to correct the problem:
Troubleshoot_FTP#Credentials_.2F_Passwords
Source: Deployment/FTP not working
Images stuck in /images/dev
Images upload and are stored in /images/dev/[mac address of host] and they're never moved to /images
Error messages on client at end of upload, being close to completed:
- FTP move failed
- FTP error
- Can't rename/move Permission Denied
- FOGFTP failed to rename file
Solutions:
- Please see Troubleshoot_FTP#Credentials_.2F_Passwords above to correct the problem.
- Ensure the permissions on /images and /images/dev are correct. See Troubleshoot_FTP#Permissions above.
- Check you "interface" setting in "Storage management"!
- For older versions of Ubuntu that have been upgraded to newer versions, this error could be caused by an older FTP setting that may be grandfather'ed in during the upgrade process.
This setting may be commented out or set to NO inside the settings file (see above), un-comment this, and set it to YES like this:
write_enable=YES
NOTE: Moving images from /images/dev to /images happens during image upload. After attempting to correct the issue, try to re-upload and see if your image gets moved.
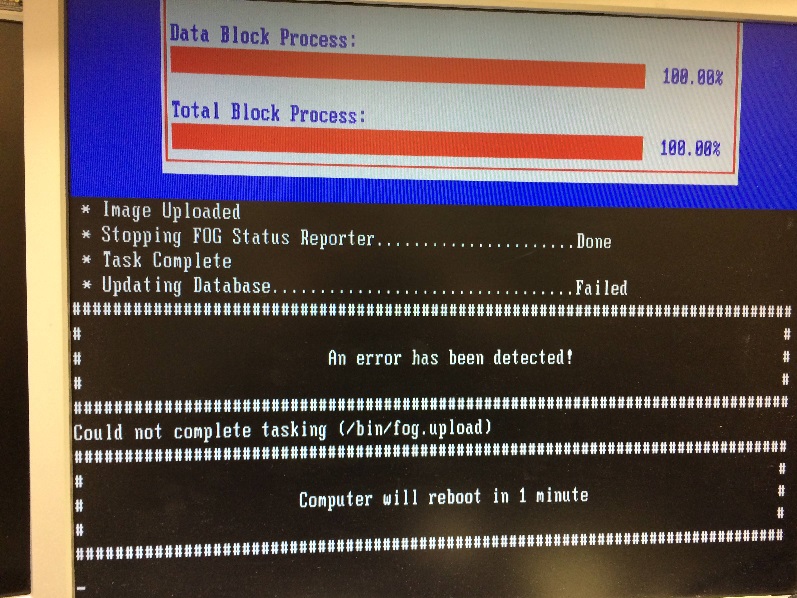
Updating Database...Failed
An image capture goes to 100% and states that the Task is complete, but then says:
Updating Database.....Failed An error has been detected! Could not complete tasking (/bin/fog.upload) Computer will reboot in 1 minute
This error is only seen in FOG 1.3.0 and up due to the complete re-write of the upload & download scripts.
Pictured below:
Solutions:
This can be FTP Credentials and Permissions related, please look to the Credentials and Permissions section above.
Large Image - Connection time out during Delete, Upload, and Replication
At first glance, this problem looks a lot like the above problem, because it will cause images to be "stuck in /images/dev", however this specific probelm is not credentials related. It's file-system related.
If your /images directory is formated with the ext3 filesystem you probably run into an issue where deleting the old image in /images/[image name] takes a very long time (minutes with 100GB+ images) and therefore the FTP connection times out and does not rename/move the newly uploaded image from /images/dev/[mac address] to /images/[image name], or may not delete the image from /images.
Solution:
The solution is to have your images on a different filesystem like ext4 or LVM. The issue is defragmentation/reallocation in ext3. For a detailed explanation see here: HOW TO REMOVE BACKUPS?
Images won't finish uploading, won't go past "Clearing ntfs flag"
This is permissions related. See forum threads for more details:
stuck-after-clearning-ntfs-flag
imaging-stuck-on-upload-after-finished
List permissions:
ls -laR /images
Fix permissions: Use the correct OS user, and correct storage node password to change ownership and give read/write/execute to everyone. Assumes user is "fog".
chown fog -R /images chmod -R 777 /images
Changing ownership with user AND group (replace "user" and "group" with actual values):
chown user:group -R /images