Difference between revisions of "Troubleshoot NFS"
(→Ubuntu) |
m (Article good enough to be called done. Just missing "enable RPC on boot" for Ubuntu.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 23:22, 27 May 2015
Contents
NFS's roles in FOG
NFS is used to transfer images to and from clients in FOG, and is used on both the client and server. The server's setting file controls what files & directories are exported, and their options. NFS allows writing to the /images/dev directory and allows reading from the /images directory. During imaging, the client mounts either /images/dev (for uploading or capturing an image) or /images (for downloading or deploying an image).
During upload/capture, NFS uploads images into a folder in /images/dev/<MAC Address Of Client> During download/deployment, NFS downloads images from /images/<Image Path>
Please note that FTP is used to move images from /images/dev to /images.
Testing NFS
Using a FOG debug deployment for testing (easy/quick way)
The first thing we must do is create a test file that we use to test with. On your FOG server:
echo 'This is the text I use to test with.' > /images/test.txt
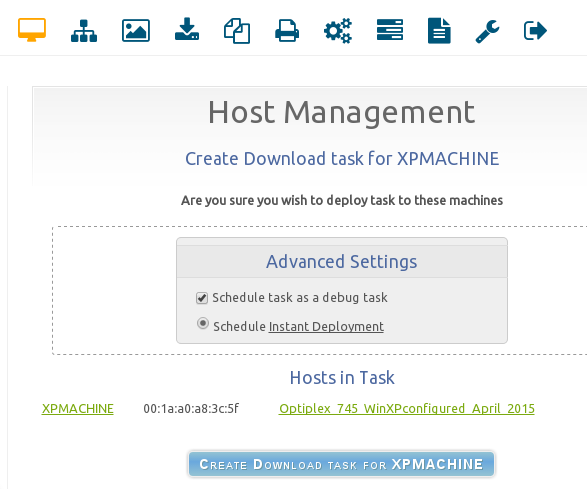
Select the problematic client from your Hosts list in the web UI, Choose "Basic Tasks", then pick download. Create an immediate debug task. See picture below:
At the client, if it did not WOL, turn it on.
After the client shows options on the screen, you can press [enter] to be given a command prompt.
You first need to create two directories to mount to:
mkdir /images mkdir /images/dev
Next, we will mount to FOG's remote image directories like this:
mount -o nolock,proto=tcp,rsize=32768,intr,noatime $storage /images mount -o nolock,proto=tcp,rsize=32768,intr,noatime 10.0.0.3:/images/dev/ /images/dev
Next, we will execute a command that will test download and upload at the same time. We will attempt to read /images/test.txt and write that file to /images/dev/test.txt
cp /images/test.txt /images/dev/test.txt
If you recieved no errors, you're probably good to go. You can confirm all went well by looking at the contents of the moved file:
cat /images/dev/test.txt
Using a separate Linux machine for testing (hard/long way)
below r3472 (1.2.0 is below r3472)
inside /etc/exports on the FOG server, Set the fsid for /images to 0 and /images/dev to 1
sudo vi /etc/exports
instructions on using Vi: Vi
Save that, exit that, then run this:
exportfs -a
Restart NFS and RPC (see services below)
After restarting NFS and RPC, proceed to the steps below just below:
r3473 and above
Linux must have an existing directory to mount remote directories to. Below, we create two directories and mount to each of them. On a separate Linux machine (not your FOG server), you can edit the "mount" command to mount a remote directory. After the mounts have been configured, we can test uploading a file and downloading a file.
At the CLI of the separate Linux machine:
Next, we will execute a command that will test download and upload at the same time. We will attempt to read /images/test.txt and write that file to /images/dev/test.txt
cp /images/test.txt /images/dev/test.txt
If you recieved no errors, you're probably good to go. You can confirm all went well by looking at the contents of the moved file:
cat /images/dev/test.txt
NFS & RPC Service
Fedora 20/21
NFS Status:
systemctl status nfs-server(should be on and green, no errors, and enabled)
The restart command is most useful, if any errors are encountered during manual start/restart, they are displayed.
systemctl restart nfs-server
Enable NFS on boot:
systemctl enable nfs-server
RPC Status:
systemctl status rpcbind
Restart RPC:
systemctl restart rpcbind
Enable RPC on boot:
systemctl enable rpcbind
Ubuntu
NFS status:
sudo service nfs-kernel-server status
The restart command is most useful, if any errors are encountered during manual start/restart, they are displayed.
sudo service nfs-kernel-server restart
Enable on boot:
update-rc.d nfs-kernel-server defaults
RPC Status:
/etc/init.d/portmap status
Restart RPC:
service rpcbind stop service rpcbind start
Enable RPC on boot:
code here
NFS Settings File
The primary NFS settings file is located here:
/etc/exports
On a standard FOG install where everything is self-contained on one system, it should look like this:
/images *(ro,sync,no_wdelay,no_subtree_check,insecure_locks,no_root_squash,insecure,fsid=0) /images/dev *(rw,async,no_wdelay,no_subtree_check,no_root_squash,insecure,fsid=1)
Creating & verifying .mntcheck files
.mntcheck is a hidden and empty file that a FOG client uses during image upload/capture and image download/deployment to verify an NFS share is mounted correctly.
To create these files, on the FOG server:
touch /images/.mntcheck touch /images/dev/.mntcheck
Verify these files with:
ls -laR /images | grep .mntcheck
This should return two results. One for /images and one for /images/dev
Disable & Verify Firewall
Fedora 20/21/22/23
Disable/stop Firewall
systemctl disable firewalld.service
systemctl stop firewalld.service
Can be undone with "start" and "enable".
Check Firewall in Fedora 20/21/22/23
systemctl status firewalld.service
Fedora 16
Add /bin/bash to /etc/shells as the vsftpd yum install does not do it correctly causing tftp timeout message
Debian/Ubuntu
sudo iptables -L
If disabled, the output should look like this:
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
Disable Ubuntu Firewall
sudo ufw disable
Disable Debian Firewall
iptables -F iptables -X iptables -t nat -F iptables -t nat -X iptables -t mangle -F iptables -t mangle -X iptables -P INPUT ACCEPT iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT iptables -P FORWARD ACCEPT
Other debian settings:
/etc/hosts.deny
This setting in the above file will deny traffic from any source except locally:
ALL:ALL EXCEPT 127.0.0.1:DENY
Comment out this line like so:
#ALL:ALL EXCEPT 127.0.0.1:DENY
Windows 7
Start -> Control Panel -> View by "Small icons" -> Windows Firewall -> Turn Windows Firewall On or Off -> Turn off all three.
Configuring firewall on Linux
To set the firewall for Linux to only allow what is necessary, please see the FOG security article.
Permissions
For the purposes of this article (troubleshooting), the /images directory should have 777 permissions set recursively.
You can do that like this:
chmod -R 777 /images
Common problems and fixes
My problem isn't in the WiKi!
If you have a problem with FOG, or have a solution to a problem with FOG, please visit the forums for help or to report your solution. We try to keep the WiKi updated with things found in the forum. You can visit the forum here: FOG Forums
Image Upload: Error Checking Mount
Please see Image Capture: Error Checking Mount