Troubleshoot TFTP
Contents
TFTP's roles in FOG
TFTP is used to download the bootfile specified by either DHCP or ProxyDHCP. TFTP is very simple and has very little protections in place; Generally read-only is preferred for files offered by TFTP, however full permissions will work too. Normally, the boot-files for FOG are located in /tftpboot
Testing TFTP
Try to get a file with Linux:
tftp -v x.x.x.x -c get undionly.kpxe Connected to x.x.x.x (x.x.x.x), port 69 getting from 10.2.1.11:undionly.kpxe to undionly.kpxe [netascii] Received 89509 bytes in 0.0 seconds [84047115 bit/s]
Try to get a file with Windows:
tftp x.x.x.x get undionly.kpxe
Testing using Windows
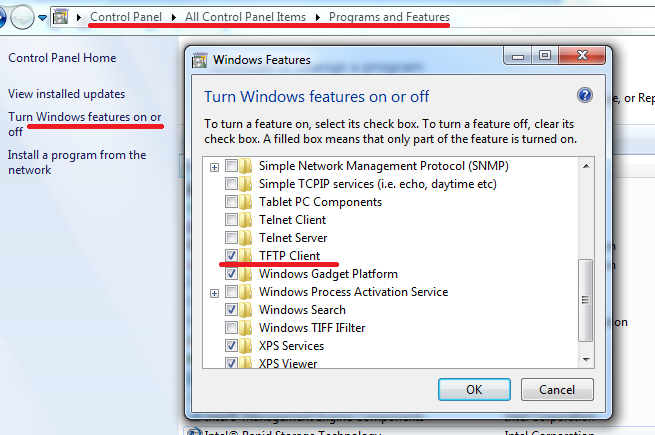
To test from windows, TFTP Client must be installed and the Firewall must allow TFTP Traffic. The best way to guarantee that your windows firewall isn't blocking TFTP is to turn it off during your troubleshooting.
Using Windows 7 Pro:
Control Panel -> Programs and Features -> Turn Windows Features on or off -> TFTP Client
TFTP Service
Fedora 20/21
status/enable/restart
systemctl status xinetd.service systemctl enable xinetd.service systemctl restart xinetd.service
Ubuntu
newer systems:
status/enable/restart
service tftpd-hpa status service tftpd-hpa restart service tftpd-hpa enable
older systems:
status/enable/restart
sudo /etc/init.d/xinetd status sudo /etc/init.d/xinetd restart sudo /etc/init.d/xinetd enable
TFTP Settings file
Fedora:
Location:
/etc/xinetd.d/tftp
To display /etc/xinetd.d/tftp:
cat /etc/xinetd.d/tftp
It should look a whole lot like this:
# default: off
# description: The tftp server serves files using the trivial file transfer # protocol.
#The tftp protocol is often used to boot diskless workstations, download configuration files to network-aware printers,
# and to start the installation process for some operating systems.
service tftp
{
socket_type = dgram
protocol = udp
wait = yes
user = root
server = /usr/sbin/in.tftpd
server_args = -s /tftpboot
disable = no
per_source = 11
cps = 100 2
flags = IPv4
}
To edit /etc/xinetd.d/tftp:
sudo vi /etc/xinetd.d/tftp
Explanation of settings for /etc/xinetd.d/tftp:
man xinetd.conf
Ubuntu:
Location:
/etc/default/tftpd-hpa
To display /etc/default/tftpd-hpa:
cat /etc/default/tftpd-hpa
It should look a whole lot like this:
# /etc/default/tftpd-hpa # FOG Modified version TFTP_USERNAME="root" TFTP_DIRECTORY="/tfptboot" TFTP_ADDRESS="0.0.0.0:69" TFTP_OPTIONS="-s"
To edit /etc/default/tftpd-hpa:
sudo vi /etc/default/tftpd-hpa
Explanation of settings for /etc/default/tftpd-hpa:
man tftpd-hpa
Instructions on using Vi:
Firewall
Fedora 20/21
Disable and stop firewall:
systemctl disable firewalld.service
systemctl stop firewalld.service
Can be undone with "start" and "enable".
Check status of firewall:
systemctl status firewalld.service
Fedora 16
Add /bin/bash to /etc/shells as the vsftpd yum install does not do it correctly causing tftp timeout message
Debian/Ubuntu
Check Debian/Ubuntu firewall:
sudo iptables -L
If disabled, the output should look like this:
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
Disable Ubuntu Firewall
sudo ufw disable
Disable Debian Firewall
iptables -F iptables -X iptables -t nat -F iptables -t nat -X iptables -t mangle -F iptables -t mangle -X iptables -P INPUT ACCEPT iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT iptables -P FORWARD ACCEPT
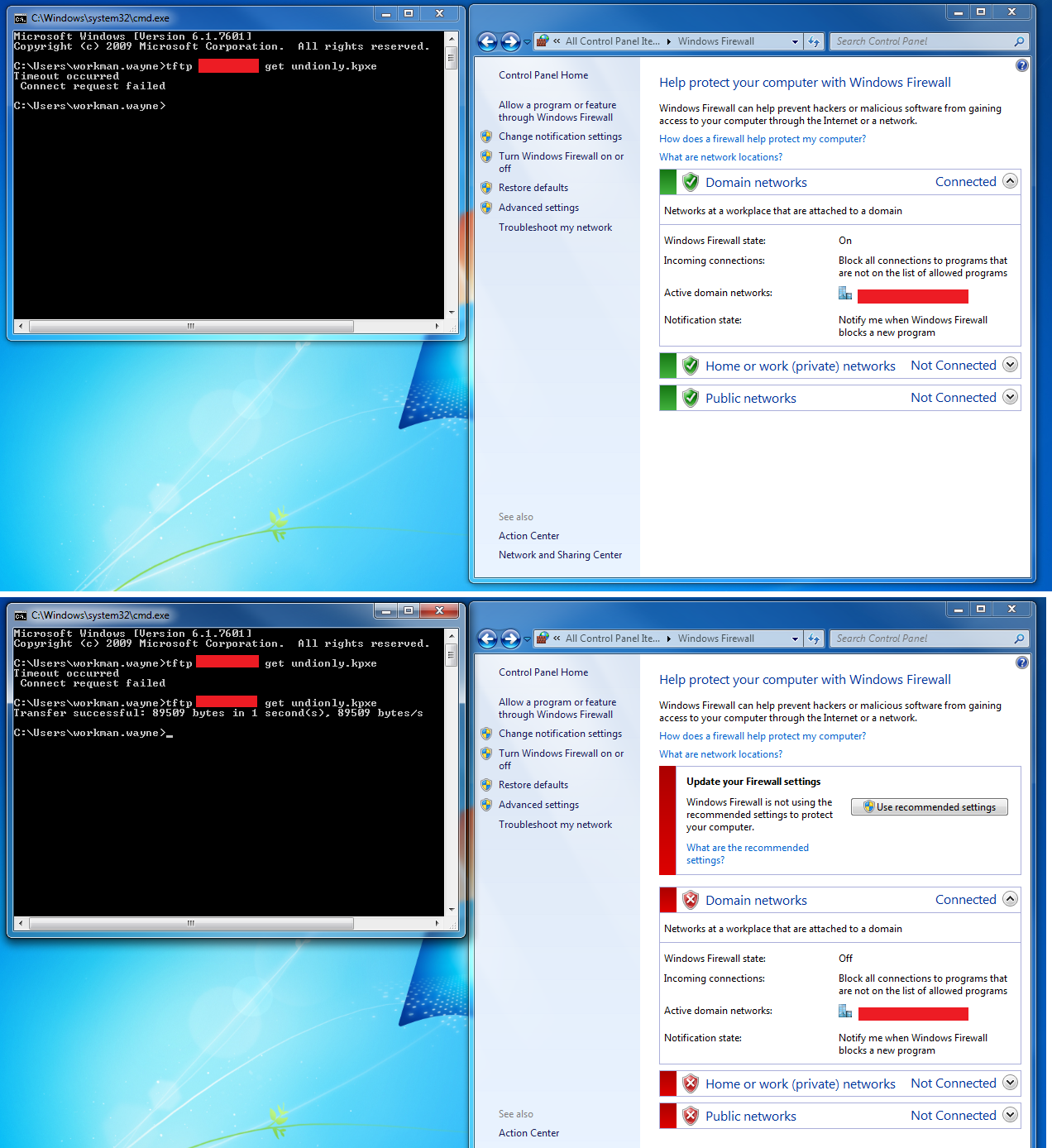
Disable Windows firewall
It's necessary to disable the Windows firewall when using windows for testing. The below image demonstrates disabling the firewall which allows TFTP traffic to pass.
Permissions
Check permissions on /tftpboot directory by using:
ls -laR /tftpboot
Set permissions to allow everyone full access to /tftpboot and all contents:
chmod -R 755 /tftpboot
See example permissions below:
/tftpboot: total 3960 drwxr-xr-x 4 fog root 4096 Apr 29 18:37 . dr-xr-xr-x. 23 root root 4096 Apr 29 18:37 .. -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 840 Apr 29 18:37 boot.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 397 Apr 29 18:37 default.ipxe drwxr-xr-x 2 fog root 4096 Apr 29 18:37 i386-efi -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 171232 Apr 29 18:37 intel.efi -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 89120 Apr 29 18:37 intel.kkpxe -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 89168 Apr 29 18:37 intel.kpxe -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 89153 Apr 29 18:37 intel.pxe -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 890208 Apr 29 18:37 ipxe.efi -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 329014 Apr 29 18:37 ipxe.kkpxe -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 329062 Apr 29 18:37 ipxe.kpxe -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 328438 Apr 29 18:37 ipxe.krn -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 329115 Apr 29 18:37 ipxe.pxe -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 123448 Apr 29 18:37 ldlinux.c32 -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 26140 Apr 29 18:37 memdisk -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 29208 Apr 29 18:37 menu.c32 -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 43210 Apr 29 18:37 pxelinux.0 -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 43210 Apr 29 18:37 pxelinux.0.old drwxr-xr-x 2 fog root 4096 Apr 29 18:37 pxelinux.cfg -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 170912 Apr 29 18:37 realtek.efi -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 90028 Apr 29 18:37 realtek.kkpxe -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 90076 Apr 29 18:37 realtek.kpxe -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 90105 Apr 29 18:37 realtek.pxe -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 170112 Apr 29 18:37 snp.efi -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 170272 Apr 29 18:37 snponly.efi -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 88763 Apr 29 18:37 undionly.kkpxe -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 88811 Apr 29 18:37 undionly.kpxe -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 88856 Apr 29 18:37 undionly.pxe -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 29728 Apr 29 18:37 vesamenu.c32 /tftpboot/i386-efi: total 1348 drwxr-xr-x 2 fog root 4096 Apr 29 18:37 . drwxr-xr-x 4 fog root 4096 Apr 29 18:37 .. -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 137280 Apr 29 18:37 intel.efi -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 812864 Apr 29 18:37 ipxe.efi -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 137664 Apr 29 18:37 realtek.efi -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 137088 Apr 29 18:37 snp.efi -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 137216 Apr 29 18:37 snponly.efi /tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg: total 12 drwxr-xr-x 2 fog root 4096 Apr 29 18:37 . drwxr-xr-x 4 fog root 4096 Apr 29 18:37 .. -rw-r--r-- 1 fog root 160 Apr 29 18:37 default
Check Network Switch settings
See IPXE for network switch settings concerning STP/portfast/etc.
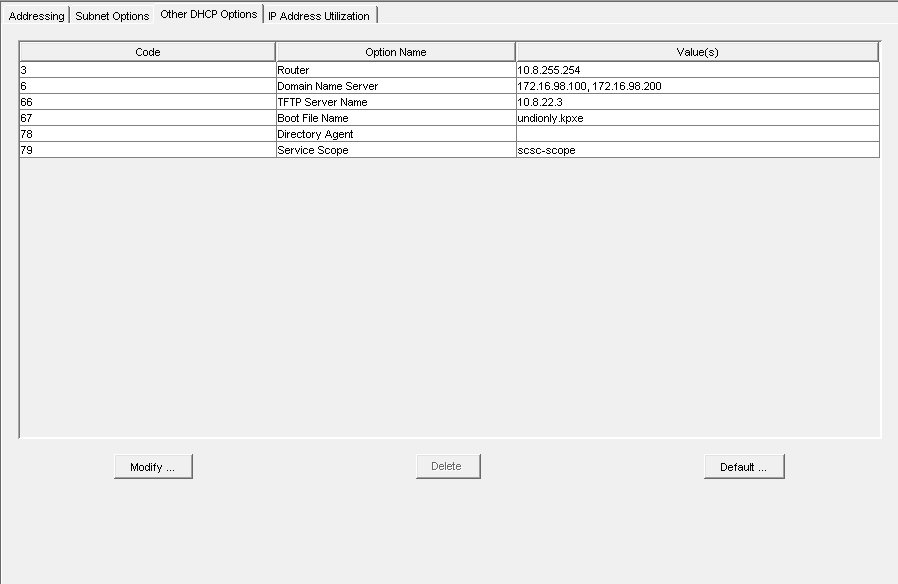
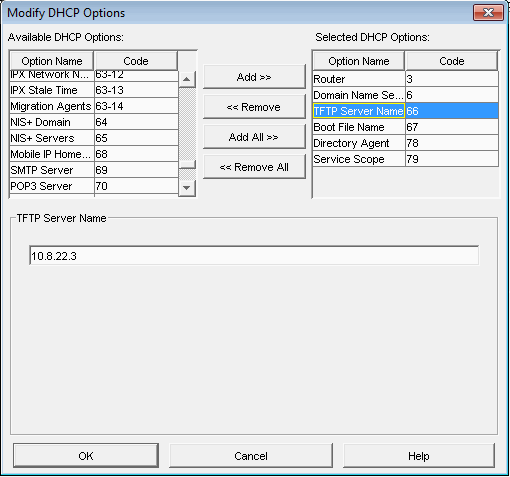
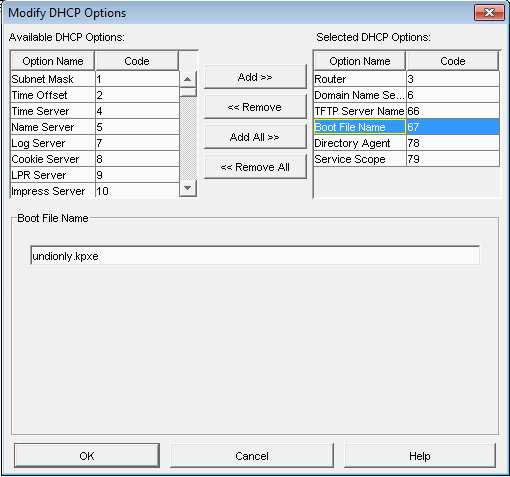
DHCP Settings
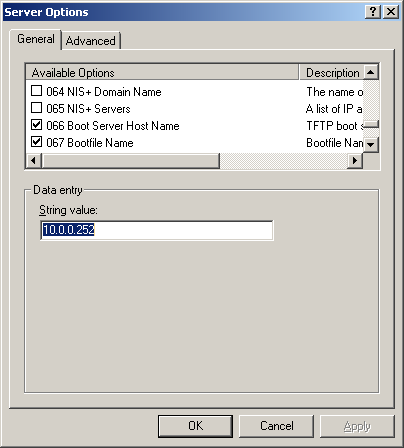
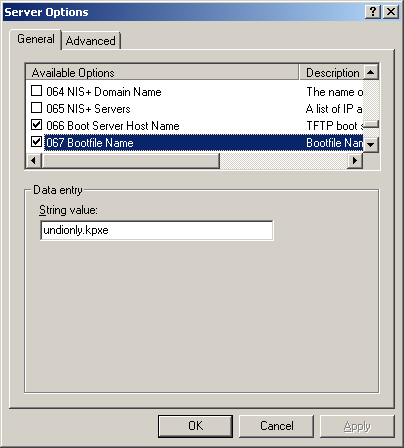
- It is important to know that versions 0.32 and below use pxelinux.0 for option 67 in DHCP
- For all versions 0.33 to current(1.3.0beta) use undionly.kpxe is generally recommended for option 67.
- Other files that can be used are listed in your directory "/tftpboot"
Linux Based (ISC-DHCP)
Articles related to ISC-DHCP
Fedora 21 Server#Verify Fedora DHCP config (if_using_DHCP)
FOG dnsmasq (ProxyDHCP)
- You would use ProxyDHCP if you do not have access to your DHCP server, or are using a device that isn't capable of specifying option 066 and 067 (next server and file name). The most popular ProxyDHCP method with fog is dnsmasq. This article will walk you through that:
- Not required unless you have an unmodifiable DHCP server/
Using_FOG_with_an_unmodifiable_DHCP_server/_Using_FOG_with_no_DHCP_server
Non-Linux DHCP
If you do not use FOG to provide DHCP services, the following sections will give some indication of settings for DHCP servers on various platforms.
Windows Server DHCP
Novell (Linux) Server DHCP
Here is a link from Novell's website on how to setup their DHCP server: http://www.novell.com/coolsolutions/feature/17719.html
MAC Server DHCP
Use OS X Server app to install and utilize DHCP.
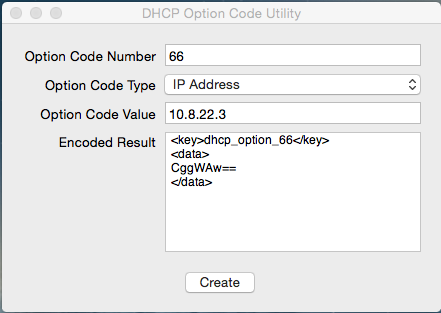
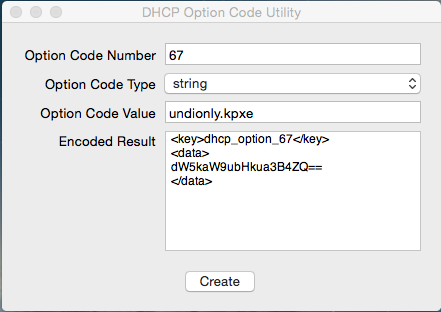
Use DHCP Option Code Utility to generate the code necessary.
https://docs.google.com/uc?id=0BwD4il5Z1G6fTmFFYU91bDNuRmc&export=download
One MUST generate the codes in order for PXE booting to work!
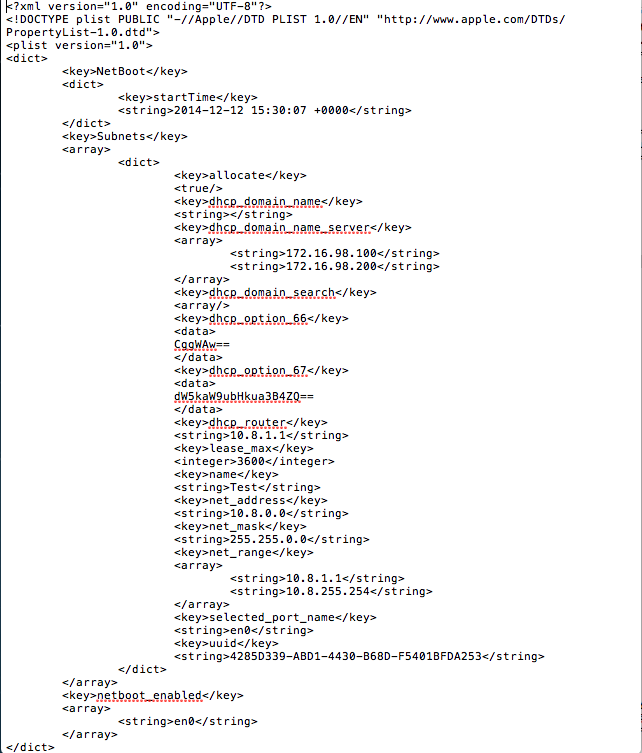
bootpd.plist is located in /etc/bootpd.plist
- Sample bootpd.plist
- This is a sample file DO NOT USE THIS IN YOUR ENVIRONMENT!!!! OS X Server app will generate most of this code for you, this example file is to show you the place where the generated code needs to be placed.
- For Reference, your generated code should be placed between "dhcp_domain_search" and "dhcp_router"
- This is a sample file DO NOT USE THIS IN YOUR ENVIRONMENT!!!! OS X Server app will generate most of this code for you, this example file is to show you the place where the generated code needs to be placed.
Other DHCP Configurations
Common problems and fixes
Unable to connect to tftp server
For Versions Before 0.24
This seems to be caused by a password issue,
1. From the fog management interface, go to users. 2. Reset the fog user password. 3. Click the "I" icon - "Other Information" 4. Click "Fog Settings" in the menu on the left 5. Replace the FOG_TFTP_FTP_PASSWORD and the FOG_NFS_FTP_PASSWORD fields under FOG settings with your Linux fog user password. (Seems like FOG_NFS_FTP_PASSWORD is gone for ver .24).
For Versions .24-.32
- Reset the local password for user fog with: [sudo] passwd fog
- In management front end, go to Storage Management -> All Storage Nodes
- Click on DefaultMember
- Change the Management Password to match the password you just changed.
- Then go to Other Information and change FOG_TFTP_FTP_PASSWORD also.
- Go to your fog web location, on Red Hat and CentOS is in:
/var/www/html/fog/
Then open the file:
/commons/config.php
and check the values of: TFTP_FTP_PASSWORD and STORAGE_FTP_PASSWORD
These MUST match the password you set above, if not write them properly in here
Finally reload of the service
/etc/init.d/vsftpd reload
Verify Server Settings
If you have modified your server setup since first install, then the new changes must be updated and verified in the Fog Settings menu. It might not be enough to just re-run the installer. For instance, a new IP lease will cause the server to show the Unable to connect to tftp server error message.
- Go to the "I" icon, which is the About menu in 0.29
- Select Fog Settings and navigate down to TFTP Settings and verify that all options are correct for your setup.
Ensure nothing else on the network is conflicting with the DHCP server
I had this error the past two days and tried all of the standard suggestions. Finally Wireshark came to the rescue. I discovered a second, feral DHCP server on the network that wasn't issuing IP addresses but must have been running interference somehow. When I disconnected it from the network, PXE boot worked as expected.