Difference between revisions of "Troubleshoot Downloading - Multicast"
(→Testing Multicast) |
(→Testing Multicast) |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
= Testing Multicast = | = Testing Multicast = | ||
| − | FOG uses udp-sender to send multicast traffic. We can test multicast functionality manually, and we will need two Linux machines to do it (your FOG server and another). The distribution doesn't matter on either, and you may live-boot a Linux disk like Fedora or Ubuntu to use as the secondary machine to accomplish this, or do a download debug task in fog as well. Ubuntu nor Fedora comes with udpcast installed but you may install it easily with <font color="red">sudo apt-get install udpcast -y</font> The command for fedora would be <font color="red">sudo dnf install udpcast -y</font> and for CentOS 7 or Fedora 21 and older it would be <font color="red">sudo yum install udpcast -y</font> | + | FOG uses udp-sender to send multicast traffic. We can test multicast functionality manually, and we will need two Linux machines to do it (your FOG server and another). The distribution doesn't matter on either, and you may live-boot a Linux disk like Fedora or Ubuntu to use as the secondary machine to accomplish this, or do a download debug task in fog as well. Ubuntu nor Fedora comes with udpcast installed but you may install it easily with <font color="red">sudo apt-get install udpcast -y</font> The command for fedora 22 and higher would be <font color="red">sudo dnf install udpcast -y</font> and for CentOS 7 and older or Fedora 21 and older it would be <font color="red">sudo yum install udpcast -y</font> |
Revision as of 22:51, 7 June 2016
Article under construction. Below, you will find notes / gibberish that I'm collecting to make into an article.
See also: Multicast
Contents
Multicast's roles in FOG
Multicasting in FOG uses UDPcast to send a single image to multiple computers using only slightly more bandwidth than sending the image to a single computer or unicast. Multicasting to many computers will be slightly slower than unicasting to a single computer.
The Basics
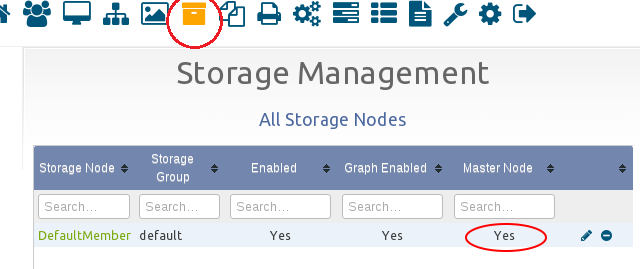
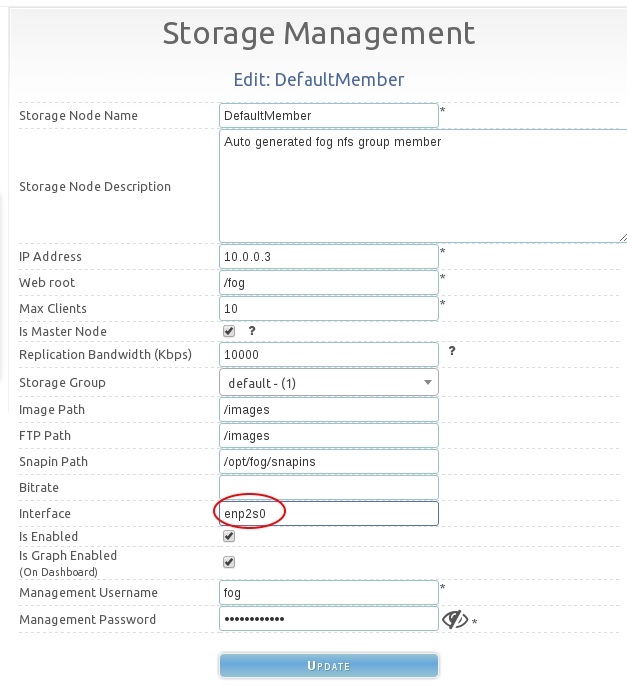
For Multicasting to work, you have to have a master storage node set, the master storage node should be a FOG server (and not a NAS), and the master storage node's interface name must be set correctly.
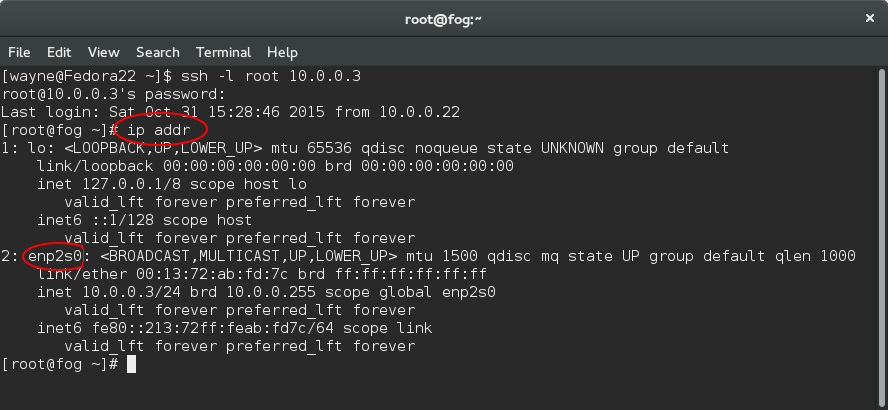
CentOS and Fedora can use weird interface names. You can get the names of the interfaces like this:
ip addr
The above command will just show the names and interface names along with some other information. From this output, you would find your interface name and set it correctly on the master storage node.
FOG version 1.2.0 has a few issues with finding the correct interface name for newer Red-Hat based systems like CentOS and Fedora. In current FOG Trunk and the future 1.3.0 release, generally the installation script does a good job at finding the correct interface name to use.
Here are some screenshots from the current FOG Trunk development (future 1.3.0) that show this process.
Below, the command to use in CentOS 7, Fedora 21, 22, and RHEL7 to find interface names.
Below, verifying that a storage node is set as a "Master".
Below, setting the interface name for a storage node.
Testing Multicast
FOG uses udp-sender to send multicast traffic. We can test multicast functionality manually, and we will need two Linux machines to do it (your FOG server and another). The distribution doesn't matter on either, and you may live-boot a Linux disk like Fedora or Ubuntu to use as the secondary machine to accomplish this, or do a download debug task in fog as well. Ubuntu nor Fedora comes with udpcast installed but you may install it easily with sudo apt-get install udpcast -y The command for fedora 22 and higher would be sudo dnf install udpcast -y and for CentOS 7 and older or Fedora 21 and older it would be sudo yum install udpcast -y
For whatever distribution you are using, it's best to turn off the firewall just for the duration of testing. You may find details about allowing multicast in the FOG security article. Find details about turning off firewall in the Disable & Verify Firewall article.
We will try to send a test file via UDP Multicast, the file we will use is a familiar one, /opt/fog/.fogsettings
On the FOG server, you would start the test with this:
udp-sender --file /opt/fog/.fogsettings --log /opt/fog/log/multicast.log --ttl 1 --nopointopoint --portbase 9000
Note we are specifying the port 9000, as this is the default used by udp-sender.
On the secondary Linux machine, we would start the receiving process with this:
udp-receiver
When a connection has been established between the receiving host and the server, you'll see a message saying it's ready to send and to press any key to continue. This message shows up on both the target host and the server, and the sending may be started from either. Once you press any key, you should see the /opt/fog/.fogsettings file's contents outputted to the screen on the receiving host.
Logs
Located here:
Web Interface -> FOG Configuration -> Log Viewer -> Multicast
And here:
Shell -> /opt/fog/log/multicast.log
Clear DB of non-essential multicast data
Inside the FOG DB, there are two multicast association tables. You can delete all the rows in those tables, re-run the FOG installer, and try again.
mysql use fog DELETE FROM `multicastSessions` WHERE 1; DELETE FROM `multicastSessionsAssoc` WHERE 1; DELETE FROM `tasks` WHERE `taskTypeID` = 8; quit
FOGMulticastManager
Check the status of FOGMulticastManager and restart:
Fedora:
systemctl status FOGMulticastManager systemctl restart FOGMulticastManager
Ubuntu:
sudo service FOGMulticastManager status sudo service FOGMulticastManager restart
Notes
Check that the interface setting for the image’s relevant storage node master is set to the actual interface name of that system. If not, change it and restart the FOGMulticastManager service.